
Scientists from Universidad Autónoma de Madrid (UAM) are analysing at the infrared microspectroscopy beamline MIRAS how plants tolerate mercury, one of the most toxic and common heavy metals founded in polluted soils.
A group of researchers has proved that franckeite, a mineral belonging to the sulfosalts family, behaves naturally as a two-dimensional material with semiconducting properties and promising applications in next-generation electronic devices, such as photodetectors or solar cells. They have been able to isolate and exfoliate ultrathin flakes of this mineral with methods compatible with large scale manufacturing. Using ALBA's synchrotron light, they could demonstrate the homogeneity of the chemical composition of individual franckeite flakes of a few atomic layers.

The infrared beamline of the ALBA Synchrotron, MIRAS, is analysing archaeological samples of two skeletons buried in a medieval church in the area of old Herzegovina. The aim of the experiment is to understand the disorders of bones. These data can provide useful information about the influence of the environment and living conditions at the middle ages at this Mediterranean area.
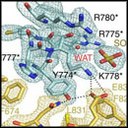
An international research lead by Institute of Biomedicine of the University of Barcelona (IBUB) and the Research Institute of the Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau (IIB Sant Pau) shows, for the first time, the three-dimensional structure of the homodimeric androgen receptor ligand-binding domain. In order to solve the 3D structure of the protein, X-ray diffraction analyses have been conducted at the XALOC beamline of the ALBA Synchrotron.
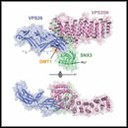
Using synchrotron light, a study led by CIC bioGUNE has described a molecular recognition mechanism which enables certain proteins of our cells to be recycled and reused. The results, published in Cell journal, open the door to biomedical applications for the treatment of pathologies like Alzheimer or Parkinson.






