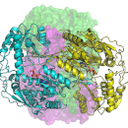
Human aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3 (ALDH1A3) is an enzyme that binds ATP, as well as a biomarker of tumor-initiating cells responsible for resistance to chemotherapy. According to a study by the UAB Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology in collaboration with the ALBA Synchrotron, their silencing restores the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapeutic agents.

Periodic lanthanide networks can bare a set of appealing properties for applications in nanomagnetism, spintronics and quantum informatics. Controlling their structural and electronic properties is of paramount importance for future applications. The multidisciplinary study performed by IMDEA Nanoscience researchers in collaboration with ALBA staff reports on the realization of erbium and dysprosium directed networks. The authors show that by supramolecular engineering it is possible to tune the electronic and the magnetic properties of the networks by switching the lanthanide metal while keeping unaltered the structural properties of the networks.

Researchers have developed a new approach to synthesis of a single-crystalline cathode material that is extremely stable with respect to internal stresses compared to the polycrystalline material, which is traditionally used. This new cathode has promising applications in the field of lithium-ion batteries for electronics, electric cars, etc. Some of the experiments were carried out at the MSPD beamline in ALBA.

Researchers propose and demonstrate for the first time a new concept for the transfer of magnetic data in three dimensions based on geometrical effects for the interconnection of functional spintronic planes. The device is based on a magnetic nanostructure and promotes the spontaneous motion of bits without the need to apply any external stimuli. This work has promising applications in spintronics. Experiments at the CIRCE beamline in ALBA were key to characterize the magnetic structures and confirm their functioning.

Sodium-sulfur batteries are promising electrical energy storage technologies that can serve as a key solution to intermittency problems and can be integrated with renewable forms of energy generation. An international research team has reported the synthesis of micro-mesoporous carbon nanospheres with continuous pore distribution as an efficient sulfur host for sodium-sulfur batteries. The work sheds new light on the progress of the sulfur cathode in sodium-sulfur batteries and provides a promising strategy for the viable design of other metal–sulfur batteries. Experiments at the CLAESS beamline in ALBA allowed determining the sulfur species during charge/discharge processes.






