ALBA Synchrotron
Marc González Cuxart from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) synthesized multiple layers of graphene films and vertical graphene nano-sheets on several substrates by means of low-pressure RF plasma in order to enhance the typical chemical vapor depositions (CVD).
In the context of the “Nanotechnology and Material Science” master and under the supervision of Eric Pellegrin and Igors Šics (ALBA Synchrotron) and Alejandro Goñi (ICMAB-CSIC), Marc González Cuxart synthesized multiple layers of graphene films (Figure 1) and vertical graphene nano-sheets on several substrates, such as HOPG, Ni(111), Ni foils and 6H-SiC(0001) by means of lowpressure RF plasma in order to enhance the typical chemical vapor depositions (CVD).
As a first approach to this technique carried out in ALBA, remote plasma was used to decouple the dissociation process of the gas from the growth process of the graphene on the substrate, to reduce the growth temperature compared to conventional CVD, and also to minimize the effect of the plasma electrical field on the orientation of the grown graphene films.
In order to assess the quality of the graphene layers, a systematic characterization process based on a sequence of several characterization tools (Raman spectroscopy, XPS, AFM and SEM) and a subsequent detailed cross-check study was carried out, including a comparison with other carbon allotropes (Figure 2). Furthermore, LEEM, PEEM and LEED measurements were carried out at the CIRCE beamline for a more complete analysis.


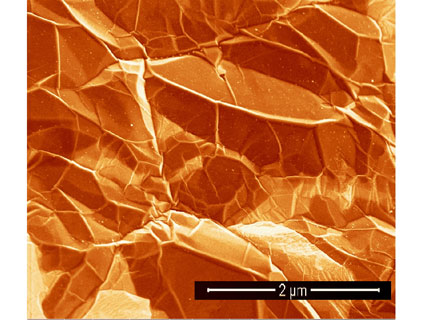
Figure 1 (left). SEM image of a graphene sample grown on Ni foil revealing a semitransparent “shrink wrap” appearance (SEM images taken at ICN2).
Figure 2 (right). Comparison between Raman spectra corresponding to different allotropes and one of our graphene samples synthesized on Ni foil (Raman data acquired at ICMAB-CSIC).